  |
This web page illustrates some applications of the CMa (Cloud Mask) CT (Cloud Type) CTTH (Cloud Top Temperature and Height) SAFNWC/MSG cloud products.
1.- Low cloud/fog identification
2.- Support to convection analysis
3.- Snow cover
4.- Desert dust identification
5.- Support to surface remote sensing
6.- Artefact removal in radar images
1.- Low clouds/fog identification
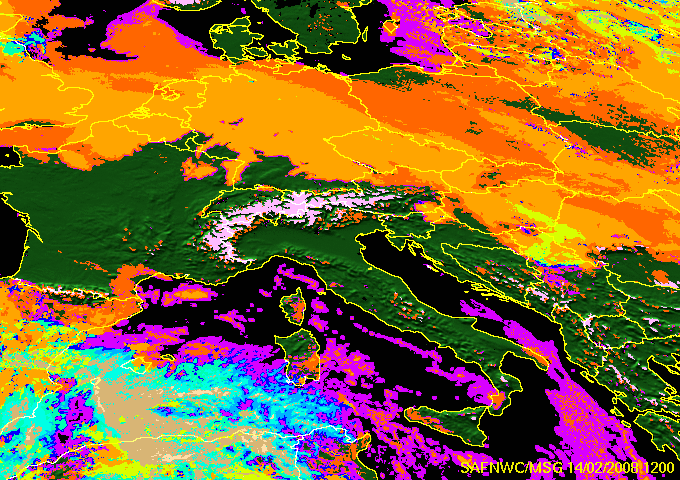
The Cloud Type (CT) allows to identify low clouds/fog in any illumination conditions. This is illustrated with a winter high pressure situation (14th February 2008) which has been documented by the Hungarian Meteorological Service on the Eumetsat web pages.
  |
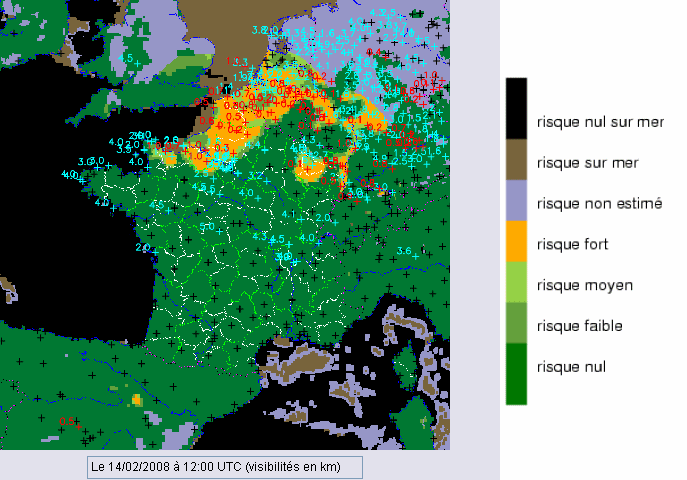
The Cloud Type can then be automatically used to map fog risks using aditional information such as NWP analysed fields (2m humidity, 10m winds). Such a merged products is routinely computed at Météo-France and is illustrated below for the 14th Fébruary 2008 12h00UTC (over land: high and low fog risk respectively in orange and green, risk not estimated in light purple), superimposed to observed horizontal visibilities (in red if lower than 1km).
 |
A temporal analysis (implemented in CT v2009) allows the detection of low clouds/fog even in twilight conditions. This is illustrated below over western Europe on 3rd April 2009: CT (with and without this temporal analysis) is compared to Eumetsat fog/low clouds RGB and natural colors RGB. The low clouds and fogs are homogeneously classified as very low/low clouds in CT whatever the illumination, whereas two RGB are needed to correctly analyse the whole scene, one for its dark portion (fog/low clouds RGB) and one for its lit part (natural colors RGB).
 |
2.- Support to convection analysis
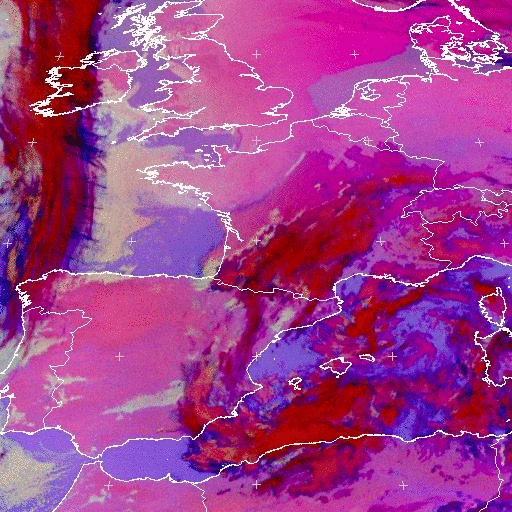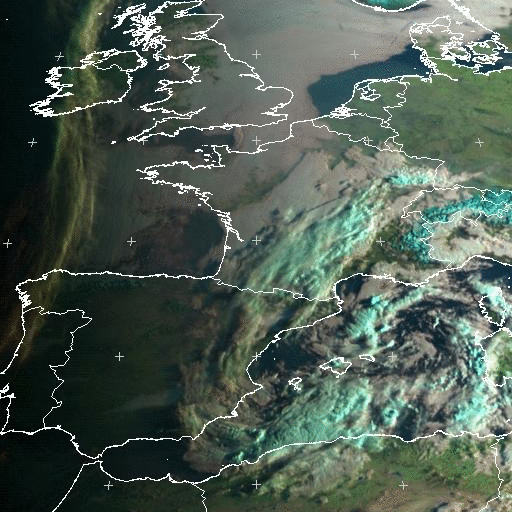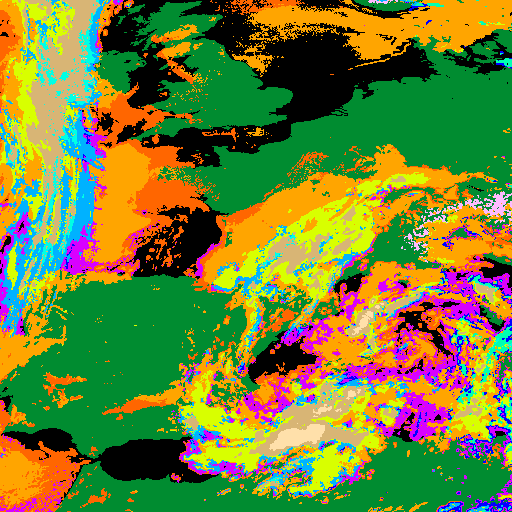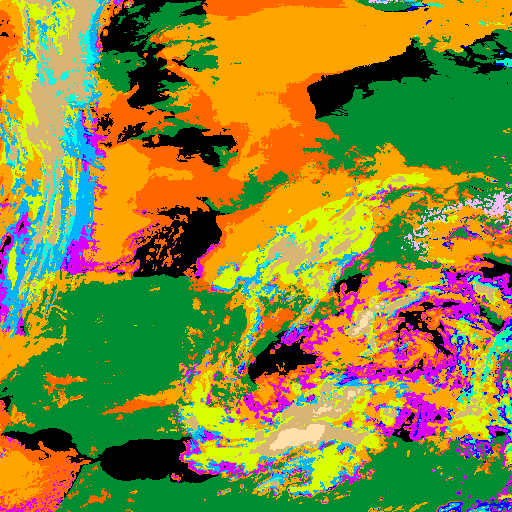
Developped convective cells are identified by high or very high clouds in the Cloud Type (CT) and their height can be obtained from the Cloud Top Temperature and Height (CTTH) product.This is illustrated with a very severe convective storms over Hungary (20th May 2008) which has been documented by the Hungarian Meteorological Service on the Eumetsat web pages.
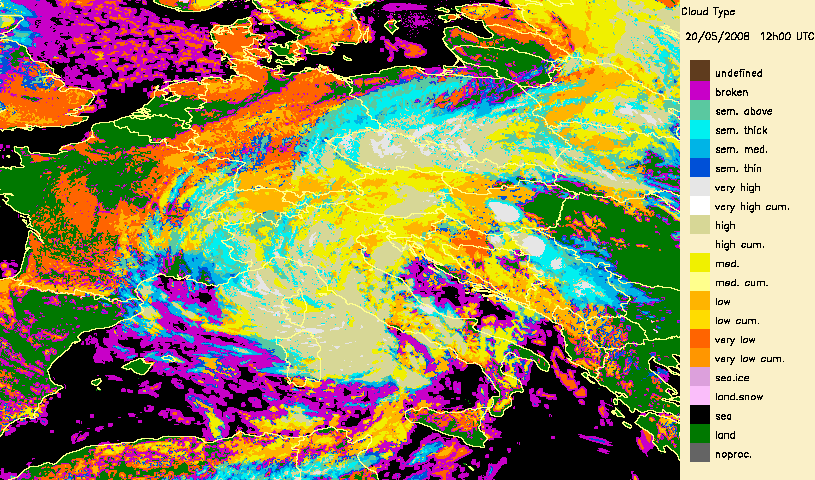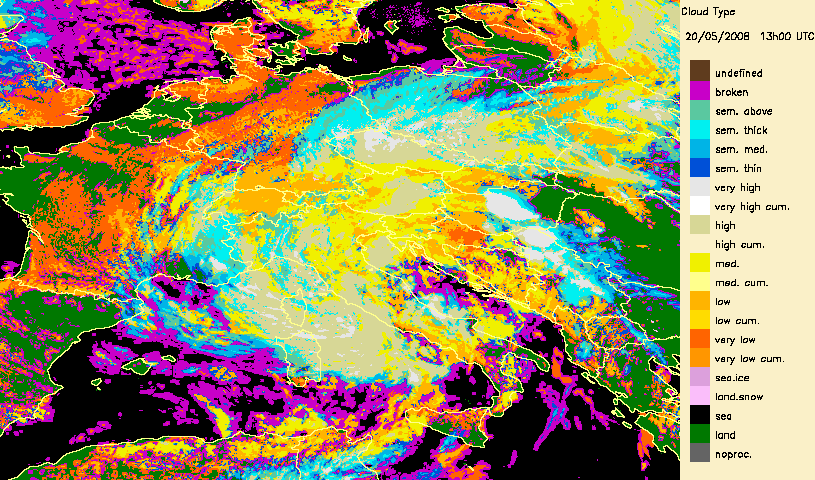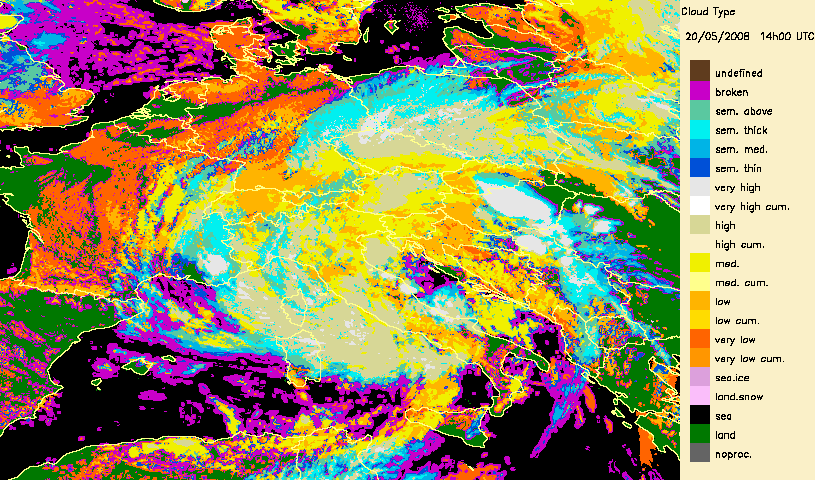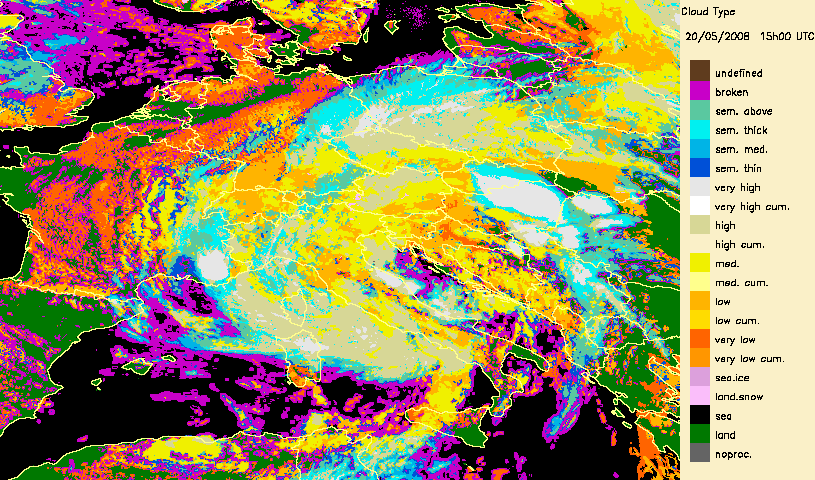 |
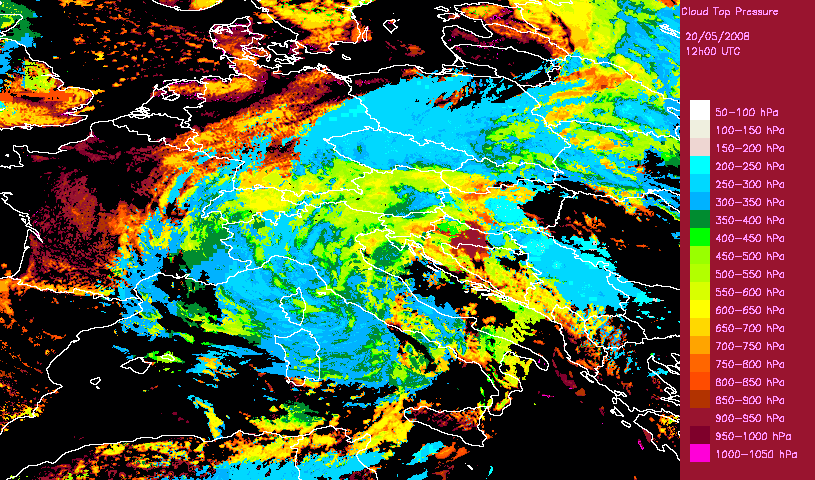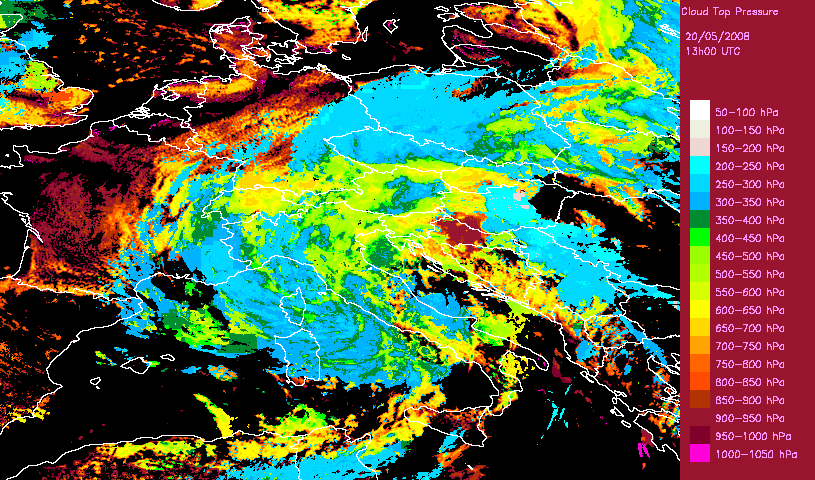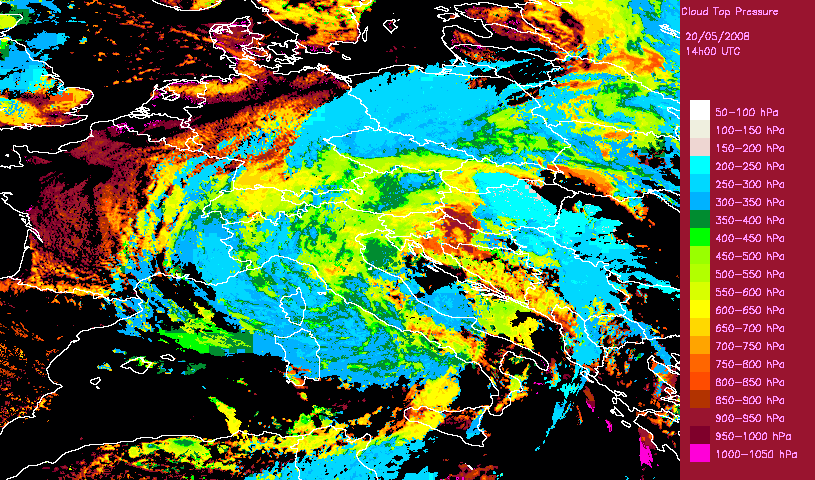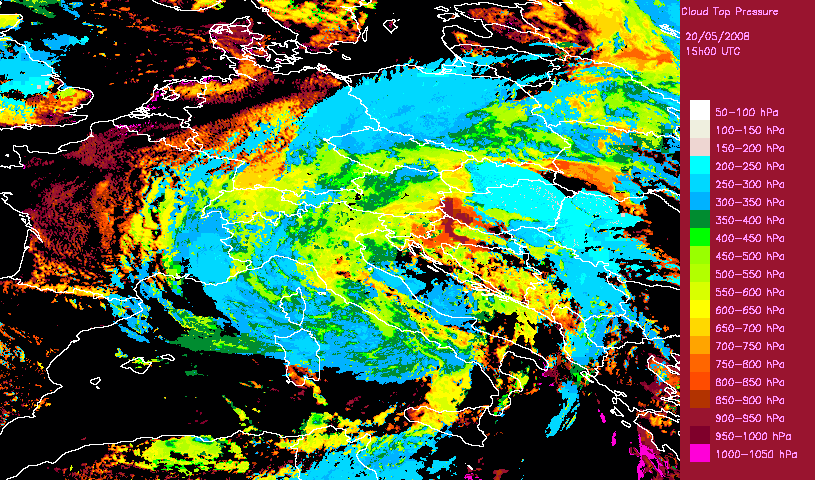 |
Cloudless snowy areas can be identified in daytime conditions by the Cloud Type CT product. Daily map of snow covered ground can then be obtained using Cloud Type derived from all individual SEVIRI slots of the day, as illustrated on the maps derived by the Hungarian Meteorological Service for 6th January 2009.
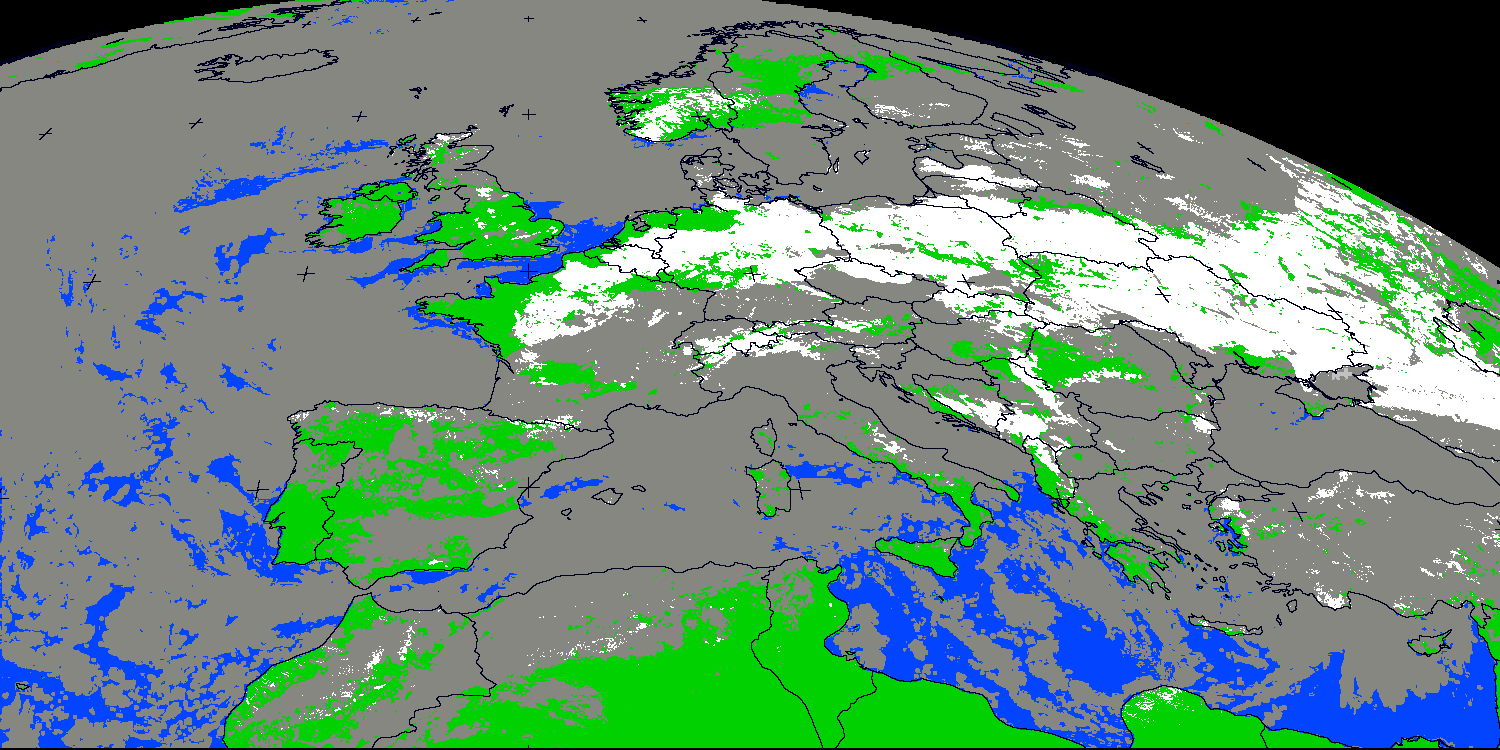 |
Daily snow composite (6th January 2009) (in white: snow at
least in one slot ; grey:: always cloudy ; green/blue: always cloud-free (without
snow)).
Courtesy of Hungarian Meteorological Service.
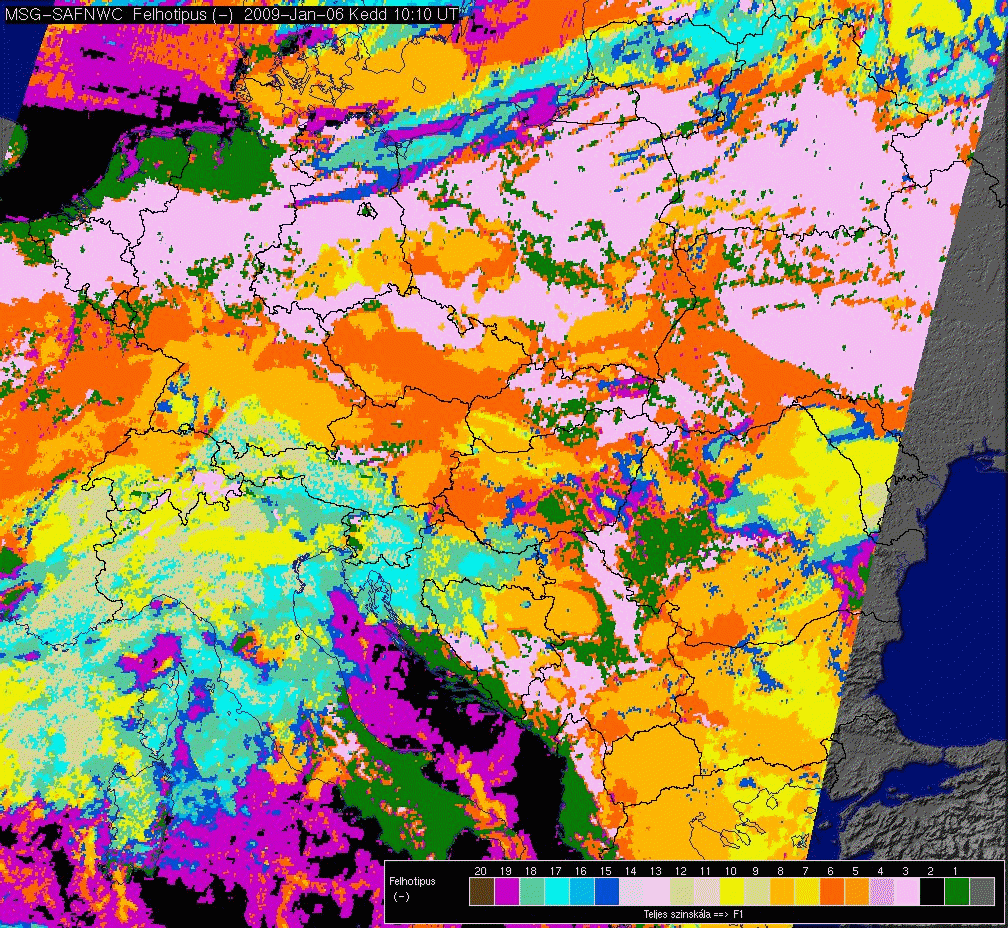 |
Individual Cloud Type (6th January 2009, 10h15) (Snow
appears in pink).
Courtesy of Hungarian Meteorological Service.
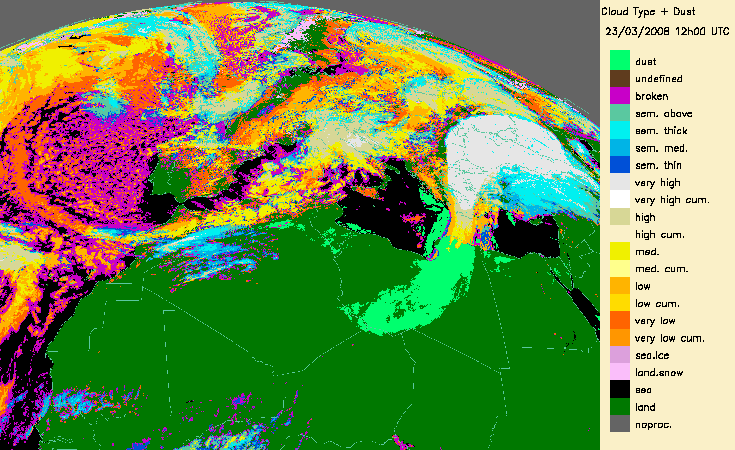
4.- Desert dust identification
The dust flag from the Cloud Mask (CMa) products allows to identify desert dust over ocean (in daytime and night-time conditions) or over continental areas (only daytime).
This is illustrated for a major transport of desert dust from West Africa to the Lesser Antilles (21-25th June 2007) (documented on a Eumetsat web page:
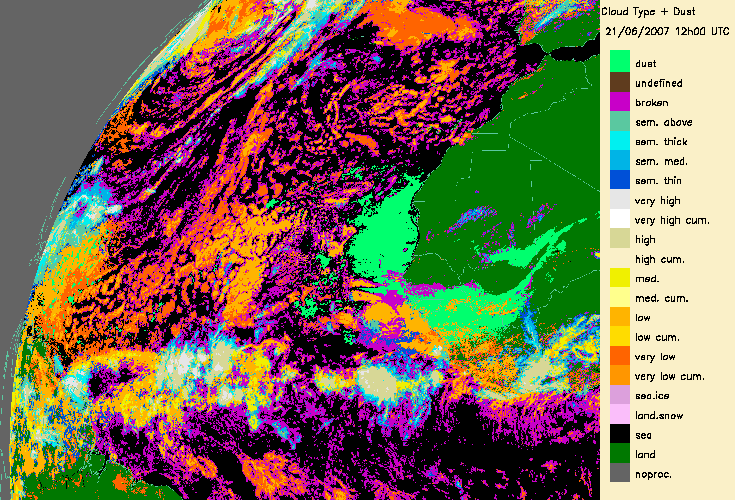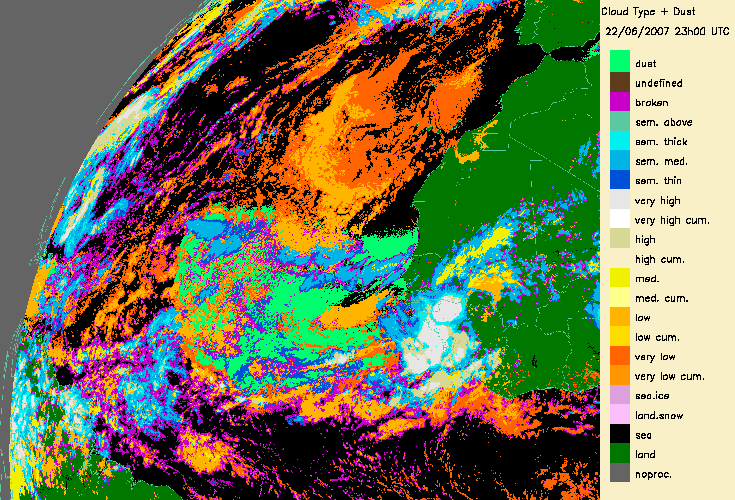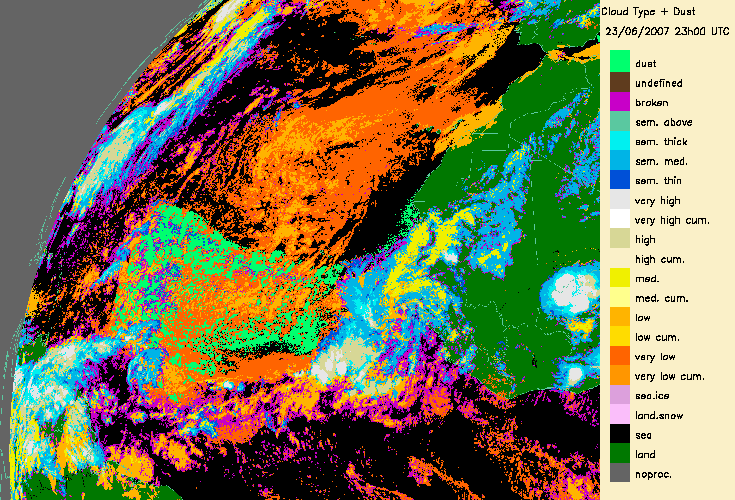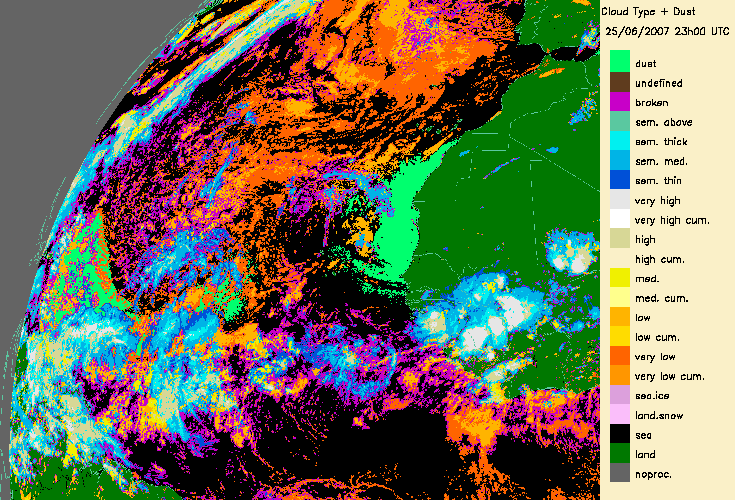 |
From 21st June 2007 to 25th June 2007
This is also illustrated with a event of coloured rain over Bulgaria due to desert dust (23rd March 2008) (also documented on Eumetsat web page:
 |
5.-Support to surface remote sensing
One obvious use of the Cloud Mask (CMa) or the Cloud Type (CT) is the identification of cloud free areas for surface remote sensing applications. It is the case for the OSI SAF for Sea Surface Temperature computation or the LSA SAF for Land Surface Temperature or surface albedo computation.
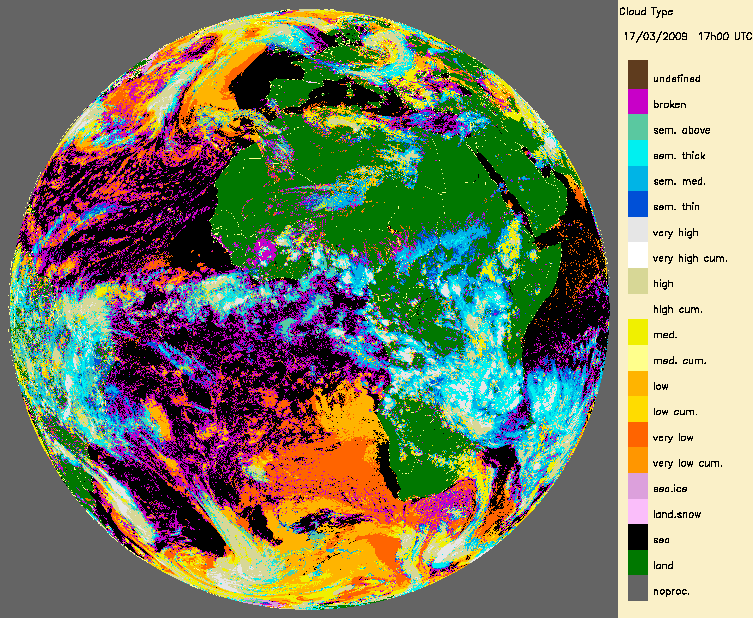 |
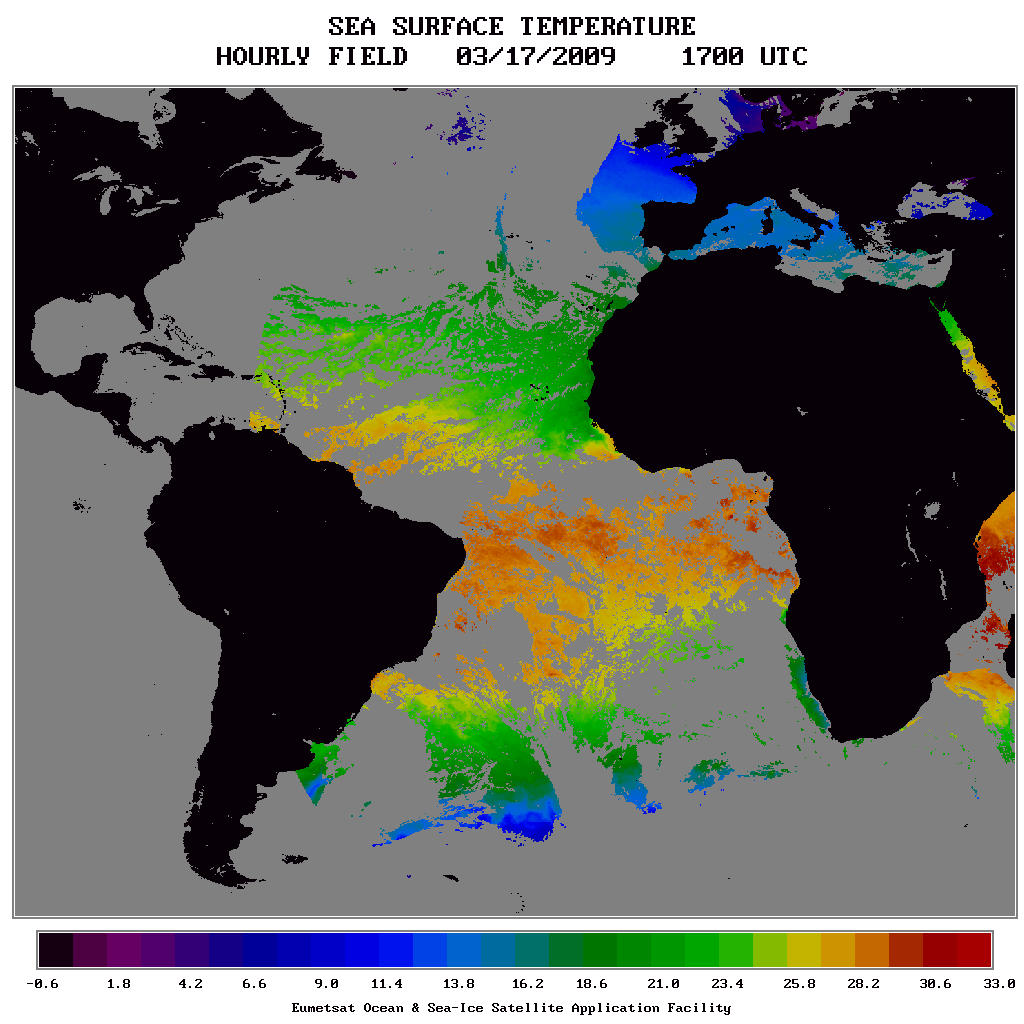 |
Example of Sea Surface temperature from OSISAF (17th March 2009 17h00)
 |
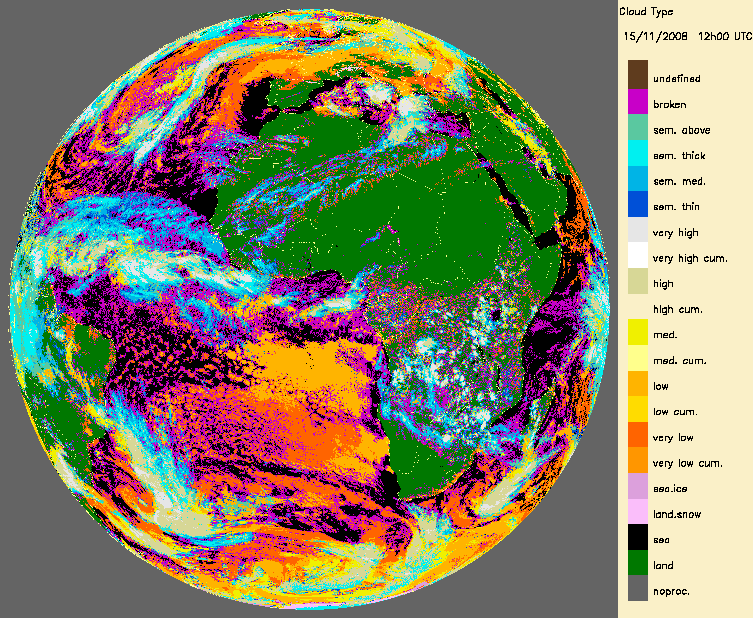 |
 |
|
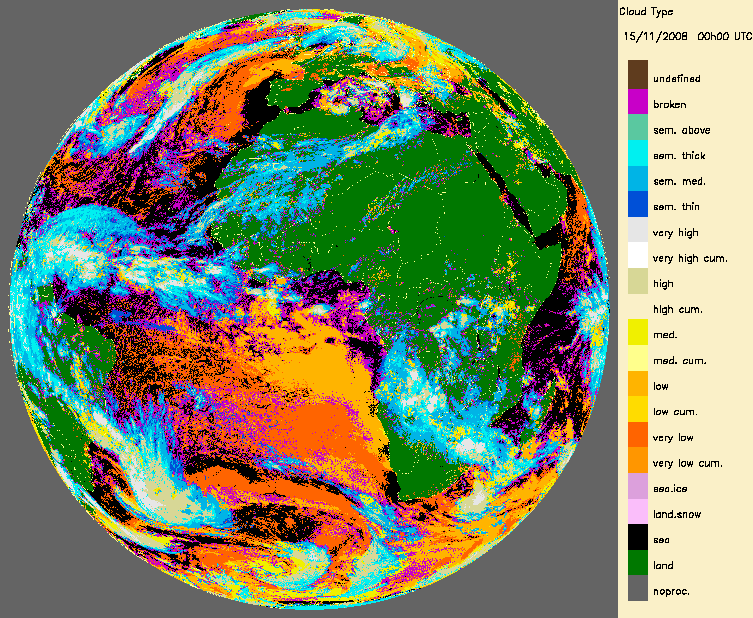
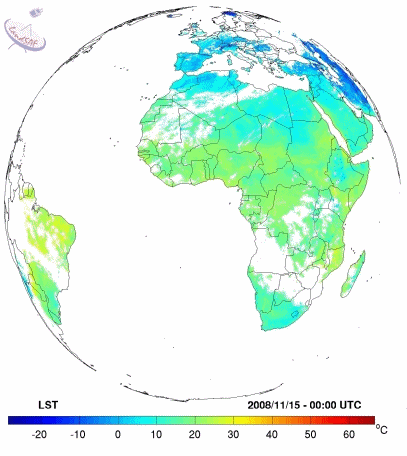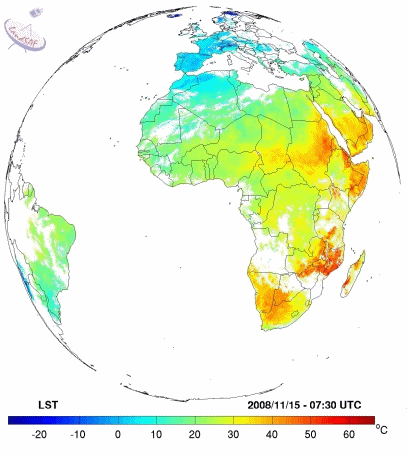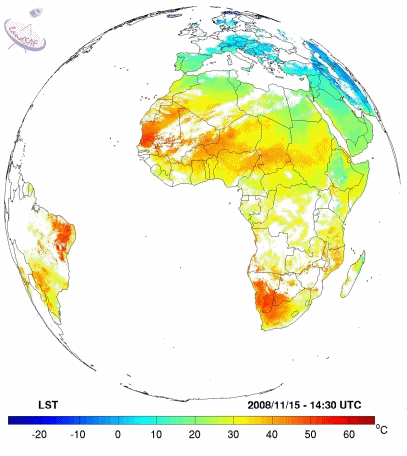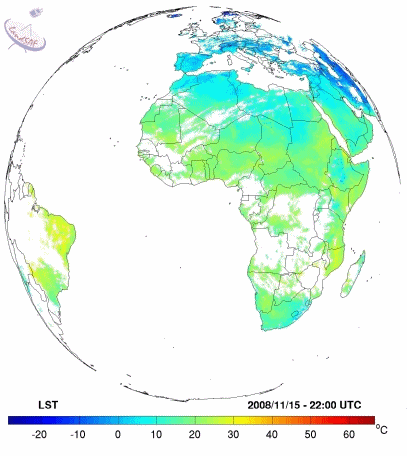
Example of Land Surface temperature from LSASAF (15th November 2008)
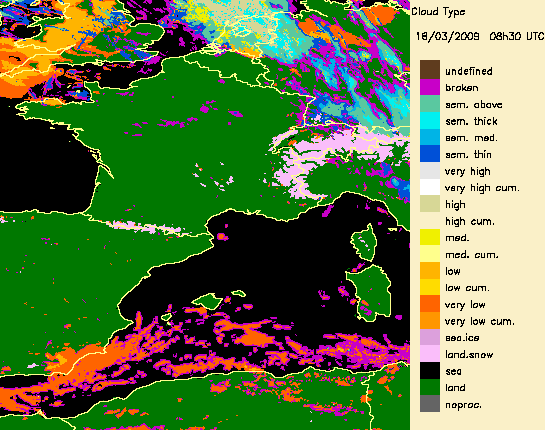
6.-Artefact removal in radar images i
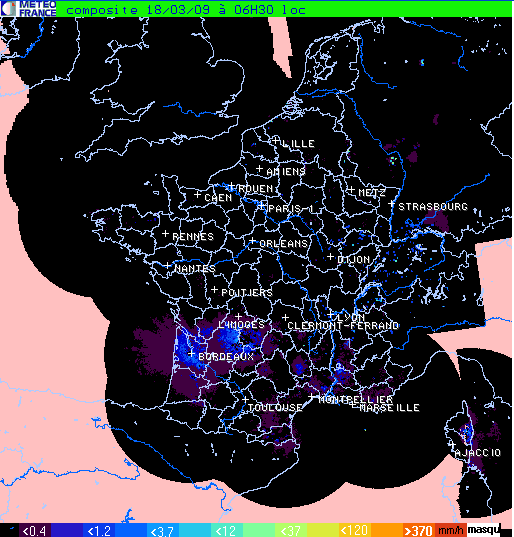
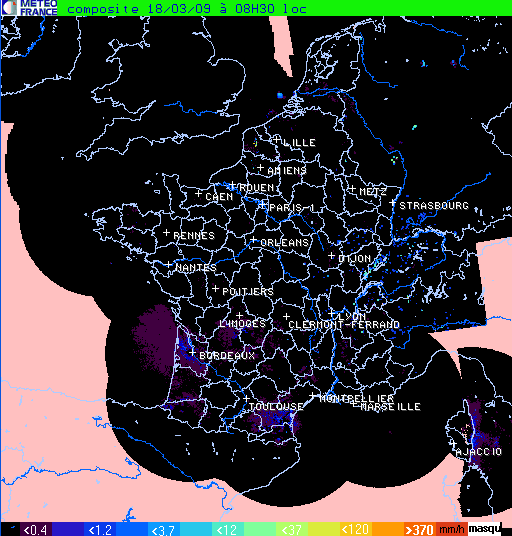
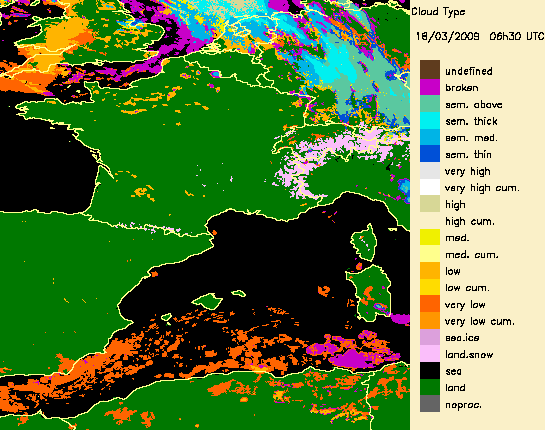
The Cloud Type product can be used to remove some artefacts in radar images. This is illustrated below with wrong radar echo in South of France.
 |
 |
 |
 |